Updated On 08, Oct 2024
An ideal education system caters to all students regardless of their learning abilities and helps them foster essential skills. However, the traditional education system is exam-centric, leading to rote memorisation and giving little to no emphasis on critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving.
Besides, standardised assessments offer limited scope for assessing students, which is why teachers cannot evaluate students’ true potential or understanding levels. Therefore, incorporating innovative methodologies like Bloom’s taxonomy is central to improving learners’s overall cognitive development and learning outcomes.
But what is Bloom’s taxonomy and what does it entail? Let us take a look:
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s taxonomy is a pedagogical framework that classifies the cognitive objectives for learning into a hierarchy. Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist, and a group of educators developed the taxonomy in the 1950s. Furthermore, the educational model categorises learning into three domains, providing a structure for teachers to evaluate students’s learning and ongoing progress. Consequently, teachers can plan lessons and develop assignments that align with the particular cognitive levels. Therefore, teachers can establish a well-planned outcome-orientated educational system, enabling students to achieve academic and individual goals.
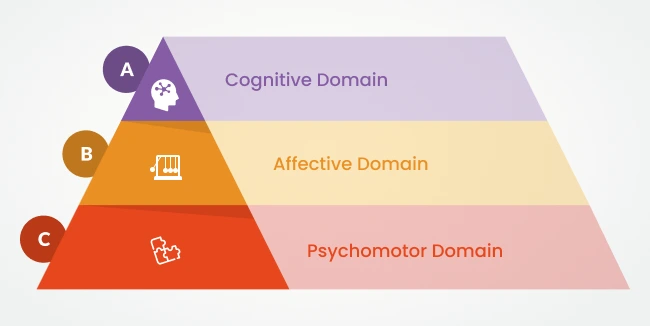
The Three Domains of Bloom’s Taxonomy
1. Cognitive Domain
The cognitive domain of Bloom’s taxonomy focuses on knowledge and intellectual skills development, and it outlines a hierarchy of six levels of thinking, which are as follows:
- Knowledge: Remembering facts, concepts, terms, and principles.
- Comprehension: Grasping an understanding of facts and information, interpreting them in one’s own words.
- Application: Applying knowledge and skills.
- Analysis: Breaking down information, understanding relationships, and making conclusions.
- Evaluation: Justifying conclusions with evidence and references.
- Creation: Creating something new by combining different ideas or concepts.
2. Affective Domain
The affective domain emphasizes the social, emotional, and attitudinal aspects of learning and includes five main aspects:
- Receiving: Acknowledging and paying attention.
- Responding: Actively participating in the learning process.
- Valuing: Accepting or rejecting ideas based on personal beliefs.
- Organising: Organising values according to situational demands.
- Characterisation: Internalisation of values, attitudes, and beliefs.
3. Psychomotor Domain
The psychomotor domain emphasises coordination, physical skills, and sensory organ movement. It focuses on developing fine motor skills (writing, drawing, using tools) and gross motor skills (throwing, running, jumping).
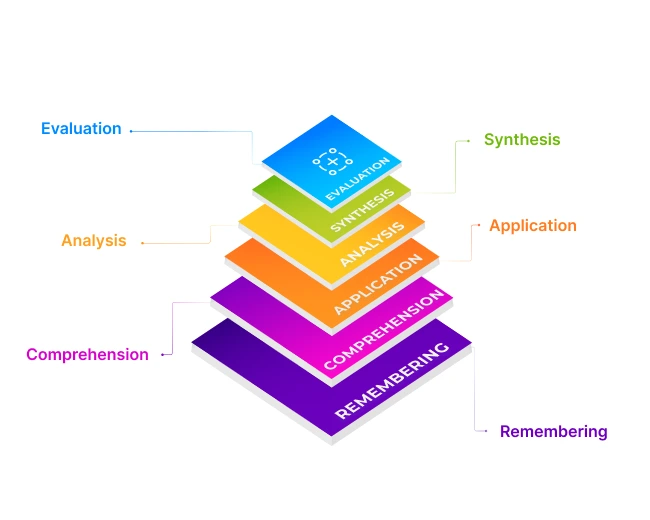
Six Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy and Its Importance
Level 1: Remember
The first level of Bloom’s Taxonomy necessitates students to recall facts, concepts, and ideas that they have learnt previously. Teachers can employ different activities that can help test students' remembering levels, such as vocabulary lists and quizzes, fill-in-the-worksheets, etc.
Level 2: Comprehension
The second level specifies the learner’s understanding level and indicates their ability to interpret information and explain concepts. Also, teachers encourage students to think more critically while applying their knowledge in various areas.
Hence, an effective evaluation technique is asking questions such as:
- Compare and contrast the characters of Caesar and Brutus.
- Elaborate the implications of World War 2.
- Briefly summarise the key points of the event.
What Is Pedagogy? Importance Of Pedagogy In Teaching And Learning Process
Level 3: Application
The third level of the taxonomy involves using existing or accumulated knowledge in new situations or applying concepts to real-world problems. For instance, learners use their mathematical skills to calculate daily expenses, distance, speed, etc.
Some simple activities that align with the application level are as follows:
- Write an essay stating a particular point of view.
- Design a marketing campaign for a new product.
- Develop a disaster mitigation plan.
Level 4: Analysis
Breaking down information and identifying the relationship between its parts is central to the fourth level of the framework. Besides, it involves students employing their analytical abilities to assess facts and situations.
Some relevant activities that align with this level are as follows:
- Debate
- Group discussions
- Identifying patterns and trends
Level 5: Synthesis
Creating something new with the help of knowledge that the learners have gathered is a crucial part of the pedagogical framework. Furthermore, students possess a certain level of aptitude, making them capable of creating something new and innovative.
Therefore, teachers can employ strategic activities such as:
- Problem-solving exercises
- Project-based learning
- Collaborative projects and assignments
Level 6: Evaluation
It focuses on evaluating concepts, ideas, decisions, and information critically and forming judgements or conclusions accordingly. Hence, it is an advanced level, wherein students develop the ability to evaluate their stance on various areas.
Teachers can include certain questions, such as:
- Judge the validity of an argument.
- Determine the best strategy for the given problem.
- Assess the effectiveness of the study plan.
Why Use Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a structured framework to design and assess learning activities, challenging students at each learning level. Teachers can use the framework to develop assessments according to the course learning objectives and desired level of mastery.
For instance, teachers can use the hierarchical levels of the taxonomy to measure the ongoing progress, ranging from the low levels to the high levels. It helps in assessing students' abilities as they advance from lower-order (understanding) to higher-order thinking skills (analysis, evaluation, and creation).
Furthermore, when they align instruction and assessment with the framework, it can ensure that students learn at a deeper level and retain information effectively. Additionally, it emphasises active learning, wherein students engage with the learning material and apply their knowledge accordingly.
Original Bloom’s Taxonomy Vs. Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
The original Bloom’s Taxonomy (1956) had knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation levels. On the other hand, the revised taxonomy (2001) includes Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyse, Evaluate, and Create.
The older version focused more on the lower-order thinking while putting less emphasis on the higher-order thinking skills. In contrast, the revised version introduced new verbs to indicate the cognitive processes like creating, evaluating, and analysing.
Moreover, it put more emphasis on creativity, identifying its relevance and importance in higher-order thinking. Also, it introduced three knowledge dimensions: declarative (factual), procedural (skills), and conditional (strategies), helping educators to differentiate between various types of skills and knowledge.
Why is Bloom’s Taxonomy Important?
Despite being more than half a century old, Bloom’s taxonomy has been a major educational framework as it provides a medium to facilitate well-thought-out teaching and learning. It helps educators establish a challenging and engaging learning environment, urging students to be more proactive in the classroom activities.
What’s more, it helps to align subject-related concepts with learning objectives, allowing instructors to monitor the ongoing progress. In addition, the taxonomy impacts different stakeholders in the following ways:
Students
- It boosts their critical thinking abilities, encouraging them to analyse and evaluate situations, facts, and concepts.
- Students become capable of self-assessing their own learning and reflecting on the major areas of improvement.
- They develop core skills like problem solving and creativity, which help them prepare for further education or employment.
Strategies For Effective Teaching Using Bloom’s Taxonomy
Teachers
- The taxonomy provides a structured framework, allowing teachers to develop strategic lesson plans that target students' cognitive abilities.
- They can use the taxonomy to implement differentiated instruction through activities that cater to students at different understanding levels.
- Teachers can develop appropriate assessments that go beyond evaluating subject-based knowledge, ensuring a comprehensive examination.
How can MasterSoft Help You In Implementing the Bloom’s Taxonomy Model?
Ensuring an enriching learning experience is a primary responsibility of teachers, and it requires incorporating innovative pedagogical methods. That is where Bloom’s taxonomy comes in, which provides a medium to deliver distinguished teaching.
However, manual methods are time-consuming and tedious; hence, instructors require advanced tools like MasterSoft’s learning management system to implement the taxonomy effectively. For example, they can use the tool to conduct online assessments in alignment with different learning levels.
Furthermore, MasterSoft’s online assessment tool is a robust tool that allows teachers to develop formative assessments with different kinds of questions.
Still wondering how to transform the teaching and learning methods of your institute? Learn More.
FAQ's on Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s taxonomy is a pedagogical framework that classifies the cognitive objectives for learning into a hierarchy. Teachers can use it to develop learning lessons and curriculum and establish learning objectives.
The importance of Bloom’s taxonomy lies in the fact that it provides a structured framework to develop and implement a well-thought-out educational process. It enables teachers to achieve a balance between relevant teaching activities and useful learning habits.
The applications of Bloom’s taxonomy are as follows:
- Curriculum Design
- Lesson Planning
- Assessment
- Teacher Training
- Differentiated Instruction
Redefine the ways of teaching and learning in your institute using Bloom’s Taxonomy
Mobile: 08448010216
Email: janki.somani@iitms.co.in














